Brewed to Perfection: Coffee Brewing Mastery
Unlock the secrets of perfect coffee brewing with expert tips, techniques, and recipes.
Blockchain: The Digital Ledger That Refuses to Forget
Discover how blockchain revolutionizes data permanence and security—uncover the digital ledger that never forgets!
How Does Blockchain Technology Work: A Beginner's Guide?
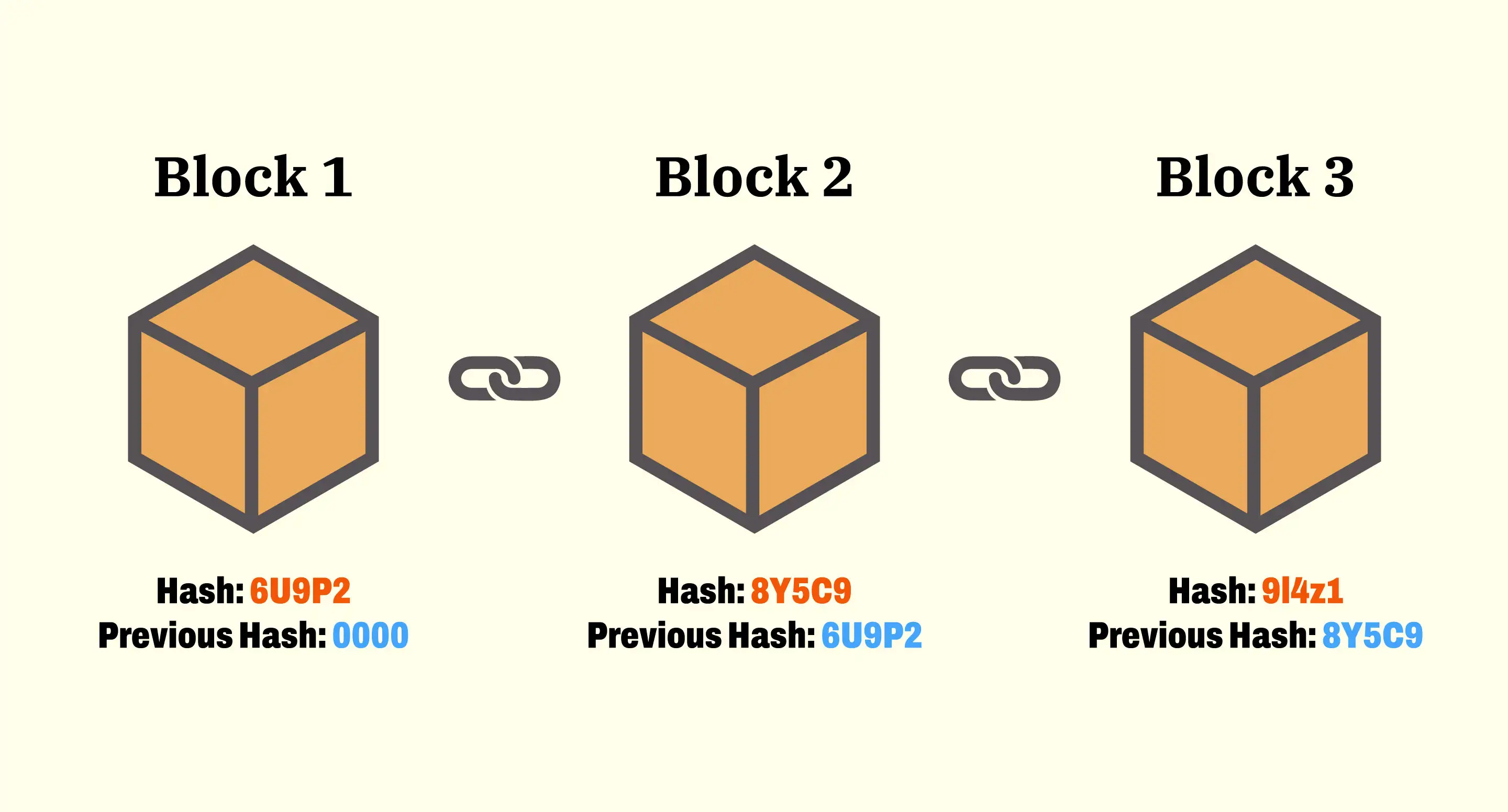
Blockchain technology operates as a decentralized digital ledger that securely records transactions across many computers. Each transaction is grouped into a block, which is then added to a chronological chain of existing blocks, creating a comprehensive history of all transactions. This process utilizes cryptographic techniques to ensure that the information is secure, transparent, and immutable, meaning once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered. As a result, it provides a high level of security and trust, eliminating the need for a central authority.
At its core, blockchain technology relies on a consensus mechanism. Participants in the network, also known as nodes, must agree on the validity of transactions before they are added to the blockchain. There are various types of consensus mechanisms, including Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, each with its own advantages and drawbacks. Additionally, blockchain enables smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code—facilitating automated and trustless agreements between parties without intermediaries.
The Benefits of Using Blockchain: Why It Matters in Today’s Digital World
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way we handle data and transactions in today's digital world. One of its most significant benefits is its ability to enhance security. By utilizing a decentralized network, data is stored across multiple nodes, making it virtually impossible for hackers to alter or manipulate information. This increases trust among users, as they can be confident that their transactions are secure and transparent. Moreover, the use of cryptographic algorithms further protects sensitive data, ensuring that only authorized parties can access it.
Another key advantage of blockchain is its ability to promote transparency and efficiency. In traditional systems, intermediaries such as banks and payment processors can slow down transactions and add extra costs. With blockchain, transactions can occur directly between parties, eliminating the need for a middleman. This not only speeds up processing times but also reduces fees associated with transactions. As a result, businesses and consumers alike benefit from the streamlined processes, leading to improved trust, reduced fraud, and overall enhanced user experience in the digital marketplace.
What Makes Blockchain Immutable: Understanding the Concept of Digital Permanence
The concept of blockchain immutability is a foundational aspect that sets it apart from traditional databases. Immutability means that once data has been recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without the consensus of the network. This is achieved through a decentralized network of nodes that validate and confirm transactions. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure and unchangeable link between them. If a hacker attempts to alter any information in a block, they would not only need to change that block, but also every subsequent block in the chain, a task that becomes exponentially difficult as the network grows.
Furthermore, the use of cryptographic techniques adds a layer of security that enhances digital permanence. The transaction data is encrypted and time-stamped, ensuring that tampering is easily detectable. Additionally, consensus protocols, such as Proof of Work or Proof of Stake, require the majority of participants to agree on any changes, further solidifying the integrity of the blockchain. This decentralized agreement framework not only fosters trust among users but also ensures that the records remain permanently available and secure, making blockchain technology a reliable solution for countless applications across various industries.